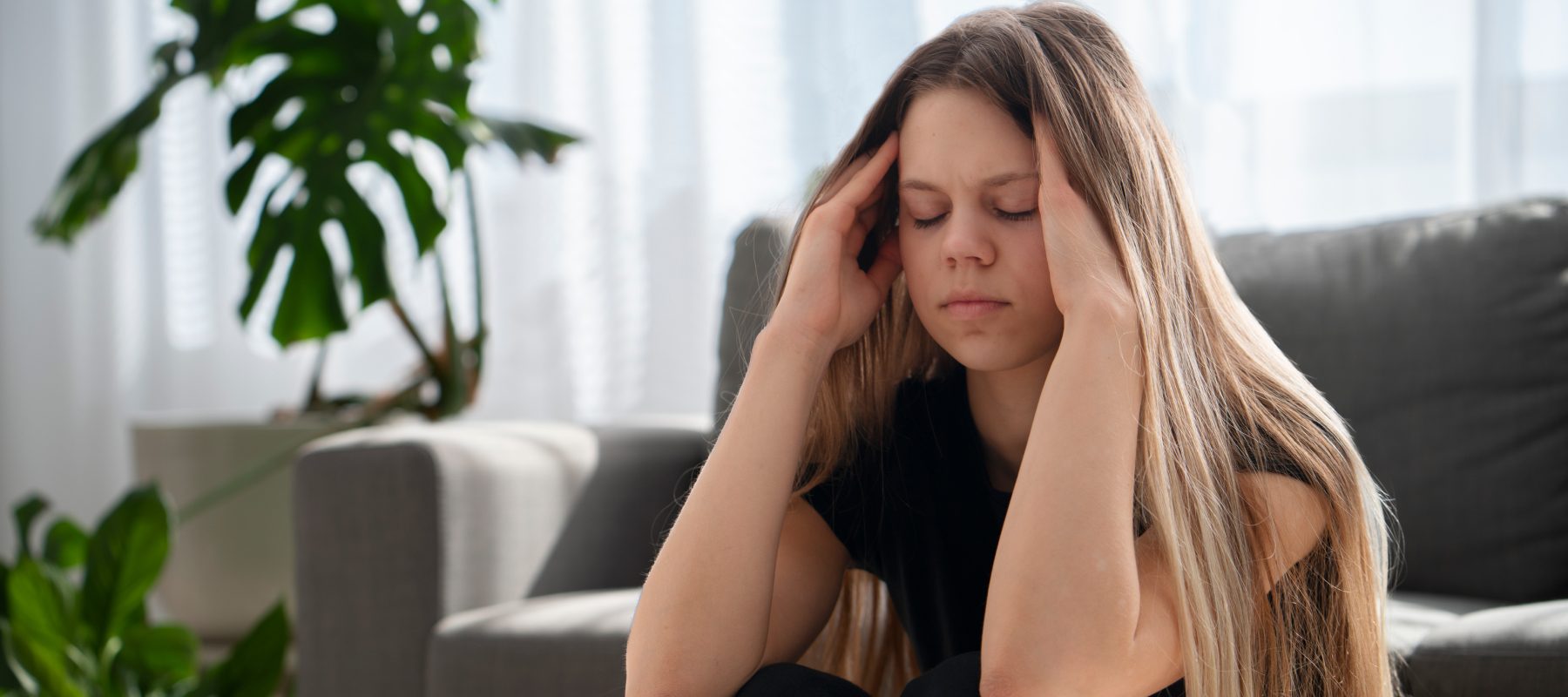
Chronic migraine is much more than just having bad headaches. The symptoms of this migraine can alter regularly or even on an hourly basis, making you stay locked in a dark, quiet room until the migraine is over.
The treatment of this situation concentrates on the diminution of the severity and frequency of the migraine.
Migraines are common worldwide and affect around 12 to 15% of the population. However, chronic migraine is less common. In fact, researchers declare that 1 to 2.2% of the global population suffers from this condition.
Chronic migraine generally affects women and people assigned female at birth or people AFAB more than men and people assigned male at birth or people AMAB. It has been found that 1.7 to 4% of women and people with AFAB possess chronic migraine, while that percentage is only 0.6 to 0.7% in the case of men and people with AMAB.
Migraine commonly starts around puberty and becomes less frequent with age. In women and people with AFAB, migraines cease entirely after menopause and rarely happen before that phase.

Symptoms of Chronic Migraine
The symptoms of chronic migraine are the same as those of episodic migraine. However, chronic migraine lasts longer and happens more often.
Chronic migraines involve headaches, although migraines are not similar to headaches. They take several forms.
The symptoms experienced from migraine to migraine generally vary, and it takes place in 4 stages, although not all migraines. Those are respectively;
Prodrome
This is reckoned as a pre-migraine stage. In addition, you can often sense insidious variations, which serve as a suggestive measure that a migraine is approaching.

Pulsating pain
Chronic migraine can be diagnosed with a continuous pulsating pain in your head. Initially, you may sense this pain only on a single side of your head. However, gradually, it spread on both sides. This pain sometimes becomes so intense that you might require a strong painkiller. However, a painkiller is never a permanent solution for such severe pain.
Aura
These symptoms occur when a migraine interrupts various areas of your brain. Auras are a bunch of visual sensations, such as random blind spots, a flashlight, and blurred images of faces and hands. Some migraine patients report experiencing auras continuously, disturbing their thought processes and contributing to excessive mental disturbance.

Headache
This is the primary painful stage of a migraine. People with chronic migraine often report experiencing continuous headaches during their migraine days. Such intense sensation often disrupts their daily routine. According to the research evidence, more than 70% of chronic migraine patients suffer from unbearable headaches. Such a condition often interrupts their routine.
Vomiting
Most Migraine patients experience a continuous feeling of nausea. This can make your migraine days even worse. Also, sometimes nausea and headache can come together. In such a condition, you must consult a doctor immediately.
Postdrome
This is when you feel the consequence or aftereffect of a migraine. The most usual terminology for this state is migraine hangover.
Migraine without aura (Lasts between 4 hours to 72 hours)
A headache meeting the following criteria;
- The pain remains on one side of the head
- The sensation feels like a pounding or a pulse.
- It becomes moderate or serious.
- Pain that aggravates basic activities.
The headache involves at least one of the following;
- Vomit
- Nausea
- Light sensitivity or photophobia
- Sound sensitivity or phonophobia
Migraine with aura
Furthermore, here are the following aura symptoms;
- Visuals like zig-zag, flash, or haze in your vision.
- Numbness or tingling in touch sensation.
- Difficulty in speech or language.
- Hemiplegia (One-sided paralysis affecting the body or face)
- Brainstem (balance difficulty, vertigo, tinnitus symptom, coordination issues)
- Partial or complete retinal effect, blindness.

Causes of Chronic Migraine
Migraine is hereditary or familial. Therefore, if you have a close biological relative with chronic migraine, you are more likely to experience it in a similar pattern.
The researchers have derived certain causes or processes that contribute to and contribute to migraines. They are as follows:
1. Blood flow changes in the brain caused by the broadening or narrowing of blood vessels.
2. Impermanent alterations that make it tough for the brain cells to comport electrical signals.
3. The alteration of brain chemistry, like shifts in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin.
4. Wrong signal emission from nerve clusters around the eyes or somewhere in the head.
5. Malfunction in signal processing centers in various parts of the brain.
6. Modifications in how the body processes and senses pain due to chronic pain.
7. Researchers have found that genetics are a non-ignorable factor in migraines. In addition, this trait can pass from generation to generation. For instance, if you have a family history of chronic migraine, there is a 55% chance that you will end up experiencing migraines at some stage of your life.
8. Women who are undergoing some severe hormonal changes often report experiencing intense migraine. Researchers have established the fact that hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and menopause have serious contributions to chronic migraine.
Prevention of Chronic Migraine
Researchers and experts do not entirely understand the cause of chronic migraines, so it is almost impossible to prevent them with 100% certainty.
Through medication, you can minimize the chance of transforming episodic migraine into chronic migraine. Additionally, a good healthcare provider can offer you the proper guidelines.

Management and Treatment of Chronic Migraine
The treatment for chronic migraine is almost similar to migraine treatment. Medications are the main form of treatment. There are also two primary treatment approaches, which are as follows;
Preventive – This medication type prevents migraines or makes them less terrible or frequent.
Rescue – This medication type rescues you by shortening the migraines.
Medical procedures are options for chronic migraine. Mental healthcare choices are also a part of the treatment.
Preventive Medication includes the following.
1. Antidepressants like venlafaxine or amitriptyline.
2. Beta-blockers like metoprolol or atenolol.
3. Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) like flunarizine or verapamil.
4. Botulinum toxin injections (Botox)
5. Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) like candesartan.
Rescue Medication includes the following.
1. Naproxen
2. Aspirin
3. Ibuprofen
Lifestyle modification
Stepping into a healthy lifestyle can reduce the symptoms of chronic migraine. For instance, incorporating these lifestyle changes—healthy eating, a balanced sleep cycle, regular exercising, and limiting alcohol and nicotine—can be highly effective.
Conclusion
Understanding, approaching, and following these facts and guidelines can help chronic migraines disappear forever with age. Make sure to adopt healthy lifestyle changes and take your medicines on time. Consider consulting a doctor if the migraine symptoms are too intense to handle. Moreover, you can live healthier without migraines with the right treatment and medical guidance.
Additionally, stay tuned to World of Heal for more health and wellness blogs and updates.
Exciting guest posting opportunities are available on our website! For details, contact us at affiliates[@]prasarnet[.]com.

Pamela is a creative content writer and editor with experience working with various multinational agencies. She is known for her dynamic approach and enthusiasm in publishing engaging and insightful articles.